
Le Centre International UNESCO-UNEVOC: Qui nous sommes | Ce que nous faisons | Nous rejoindre | Nous contacter
Le Réseau UNEVOC: En savoir plus sur le Réseau | Répertoire du Réseau UNEVOC
Espace Membres: Tableau de bord du Centre UNEVOC
Domaines thématiques: Inclusion et jeunes | Innovation et avenir de l'EFTP | Engagement du secteur privé | Les ODD et l'écologisation de l'EFTP
Nos programmes et projets clés: BILT: Connecter innovation et apprentissage | Renforcer la résilience de l’EFTP | Programme pour le leadership en EFTP | Journée mondiale des compétences des jeunes
Activités passées: Réponse COVID-19 | i-hubs: Former des pôles d'innovation | Forums mondiaux de l'EFTP | Conférences virtuelles | YEM Portail de connaissances
Nos services et ressources: Publications | Forum TVET | Profils nationaux d'EFTP | Glossaire TVETipedia | Pratiques prometteuses | Toolkits for TVET Providers | Formation à l’entrepreneuriat
Journal et événements: Grandes Manifestations EFTP | Journal UNEVOC

La transformation numérique entraîne des changements massifs des ensembles de compétences requises pour le travail et la vie. La bonne utilisation des technologies numériques est également un facteur essentiel de la réalisation des Objectifs de développement durable. L’enseignement et l’apprentissage doivent répondre aux changements et aux défis résultant de l’introduction des technologies de l’information et de la communication (TIC) dans la quasi-totalité des domaines. Les institutions d’EFTP doivent utiliser au mieux les nouvelles technologies pour dispenser un enseignement approprié. Comme le disait Bill Gates: "Il faut que les enseignants intègrent pleinement la technologie dans le curriculum au lieu d’y voir quelque chose d’additionnel, d’accessoire ou de spécial." C’est particulièrement vrai dans l’EFTP, où il s’agit de préparer les apprenants au monde du travail actuel et futur.
Les institutions d’éducation et de formation de tous niveaux doivent transmettre à chaque citoyen les connaissances, les compétences et les attitudes de même que les possibilités d’apprentissage tout au long de la vie nécessaires pour vivre et travailler dans un environnement de plus en plus axé sur la technologie. Les TIC peuvent être un puissant outil contribuant à ouvrir l’accès universel à l’éducation et à la formation. Tous les citoyens doivent posséder des compétences pour le XXIème siècle, y compris compétences élémentaires en TIC, mais des techniciens qualifiés dotés de compétences informatiques spécialisées sont aussi absolument nécessaires partout dans le monde. Pour que les systèmes d’EFTP suivent le mouvement, et pour garantir des processus d’apprentissage inclusifs accessibles à un nombre croissant d’apprenants, il sera capital de développer une culture de partage et d’ouverture. Dans un monde où les changements se produisent plus vite que jamais auparavant, les enseignants eux-mêmes ne sont pas moins des apprenants que leurs élèves. Dans le monde d’aujourd'hui, les réseaux sont devenus la ressource la plus importante - que ce soit hors ligne ou en ligne.
Les réseaux sont la ressource la plus importante
L’UNESCO-UNEVOC vise à promouvoir le recours à la technologie:
Alors qu’apparaissent des outils et technologies nouveaux pour transmettre de nouvelles compétences et dispenser la formation professionnelle, le rôle des enseignants et des formateurs évolue lui aussi sans cesse. La technologie peut introduire de nouveaux paradigmes d’apprentissage, mais elle ne saurait remplacer les enseignants et les formateurs. C’est toujours à eux que reviendra le rôle essentiel pour l’introduction des TIC dans les environnements d’apprentissage. Ces dernières années, des ressources d’apprentissage en quantité considérable sont devenues disponibles en ligne pour les enseignants, les formateurs et les apprenants. À l’UNESCO-UNEVOC, nous travaillons pour repérer les tendances émergentes, les nouvelles méthodes et les moyens d’intégrer la transmission de l’EFTP dans des contextes tant formels qu’informels: en classe, dans des ateliers, en entreprise. Nous nous attachons à identifier les compétences numériques essentielles et les aptitudes dont les enseignants de l’EFTP ont besoin pour toujours être prêts pour l’avenir.
Open Educational Resources are teaching and learning materials that one can freely use and reuse, without charge.
Les ressources éducatives libres sont des matériels d’enseignement et d’apprentissage que chacun peut utiliser et réutiliser librement et gratuitement.
On trouve en ligne une profusion de matériels d’enseignement et d’apprentissage. Les technologies numériques et Internet permettent une mise en commun toute simple de ces ressources. L’exemple de Wikipédia montre la puissance de l’édition collaborative pour la création commune de ressources cognitives ouvertes. Toutefois, les matériels éducatifs sont la plupart du temps encore publiés sous réserve de droits d’auteurs restrictifs traditionnels interdisant leur diffusion et leur réédition. L’idée de la licence ouverte vise à prendre le contrepied de la restriction résultant du droit d’auteur: au lieu de toujours imposer de demander l’autorisation du détenteur du droit d’auteur, une licence ouverte spécifie expressément dans quelles conditions une œuvre peut être utilisée et réutilisée – elle encourage ainsi le partage des ressources. En fin de compte, elle aboutit à une pédagogie basée sur les REL![]() . Dans l’EFTP, le potentiel des REL et des pratiques éducatives ouvertes ne s’est pas encore déployé. L’accès à un EFTP de haute qualité pourrait se trouver considérablement amélioré si des contenus de haute qualité étaient disponibles sous licence ouverte. Les REL peuvent revêtir différentes formes, depuis des manuels jusqu’à des curricula, des cursus, des matériels pédagogiques ou notes de conférences, des devoirs, des tests, des dossiers audio, vidéo et d’animation.
. Dans l’EFTP, le potentiel des REL et des pratiques éducatives ouvertes ne s’est pas encore déployé. L’accès à un EFTP de haute qualité pourrait se trouver considérablement amélioré si des contenus de haute qualité étaient disponibles sous licence ouverte. Les REL peuvent revêtir différentes formes, depuis des manuels jusqu’à des curricula, des cursus, des matériels pédagogiques ou notes de conférences, des devoirs, des tests, des dossiers audio, vidéo et d’animation.

Le terme ressources éducatives libres est apparu en 2002. Des conférences ont plus tard reconnu que les REL peuvent jouer un rôle essentiel dans la réalisation du Programme de développement durable à l'horizon 2030, et surtout de l’Objectif de développement durable 4 relatif à la qualité de l’éducation. Le premier Congrès mondial des REL, en 2012, a appelé les gouvernements à faire en sorte que les dépenses publiques aboutissent à la création de matériels éducatifs publics:
Les gouvernements/les autorités compétentes peuvent procurer des bienfaits substantiels à leurs concitoyens en faisant en sorte que les matériels éducatifs élaborés avec des fonds publics soient disponibles sous licence ouverte (avec toutes les restrictions qu’ils jugeront nécessaires) afin de maximiser l’impact de l’investissement (2012 Déclaration de Paris sur les REL 2012
.![]() )
)
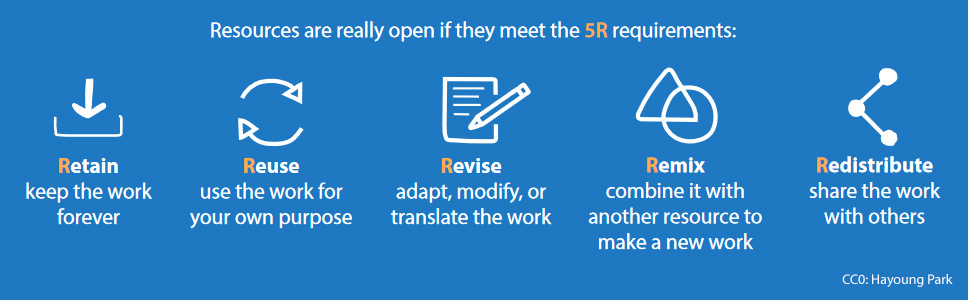
À la Conférence générale de l’UNESCO de novembre 2019, les États membres ont adopté une Recommandation sur les ressources éducatives libres![]() . Ce nouvel instrument normatif a cinq objectifs: (i) renforcer les capacités des parties prenantes pour créer, consulter, réutiliser, adapter et redistribuer les REL, (ii) élaborer des politiques d’accompagnement, (iii) favoriser un accès effectif, inclusif et équitable à des REL de qualité, (iv) favoriser la création de modèles de durabilité pour les REL, (v) promouvoir et renforcer la coopération internationale.
. Ce nouvel instrument normatif a cinq objectifs: (i) renforcer les capacités des parties prenantes pour créer, consulter, réutiliser, adapter et redistribuer les REL, (ii) élaborer des politiques d’accompagnement, (iii) favoriser un accès effectif, inclusif et équitable à des REL de qualité, (iv) favoriser la création de modèles de durabilité pour les REL, (v) promouvoir et renforcer la coopération internationale.
Une étude réalisée pour l’UNESCO-UNEVOC en 2018 a constaté que la notion de REL est encore largement inconnue chez les parties prenantes de l’EFTP – tandis qu’elle est en même temps considérée comme extrêmement prometteuse pour l’amélioration de l’accès à un EFTP de haute qualité. Notre brochure veut aider à comprendre et utiliser les REL.
Handbook: Open Educational Resources for skills development
Digital technology is gaining in importance - not only in life and work, but also in education and training. The availability of quality educational materials to prepare learners for work and life is a key factor to ensure an inclusive and equitable ...
On trouve en ligne une profusion de matériels éducatifs et de formation. Nous avons compilé une liste commentée de plates-formes de REL (en anglais) et de services fournissant des contenus sous licence ouverte pour l’EFTP.
En savoir plus sur nos travaux dans les domaines thématiques transversaux suivants:
ICT CFT/OER Hub - Online resource
This hub contains collections of Open Educational Resources (OER) curated by UNESCO and partner countries, which are aligned with the UNESCO ICT Competency Framework for Teachers (CFT). Here you can discover content and connect with other educators w ...
Publicly available generative AI (GenAI) tools are rapidly emerging, and the release of iterative versions is outpacing the adaptation of national regulatory frameworks. The absence of national regulations on GenAI in most countries leaves the data p ...
Guidelines for countries to undertake a strategic planning framework
These guidelines follow the publication of Digital Transformation of TVET and Skills Development Systems in Africa - Guidelines for countries to undertake a situational analysis (‘the Situational Analysis Guidelines’).
In concert with the situ ...
Guidelines for countries to undertake a situational analysis
The Pan African Initiative for the Digital Transformation of TVET and Skills Development Systems in Africa (‘the initiative’) was launched on 9 March 2021. The initiative’s overall objective is to create an ecosystem that will enable and accele ...
While the key role of digital competence is well-acknowledged in meeting the needs of Industry 4.0 and the new demands of the digital economy and society, COVID-19 has exposed, with urgency and intensity, the importance of building digital competence ...
Digitalization has led to extensive changes in the skills required for work and life. For technical and vocational education and training (TVET) institutions to remain relevant and attractive, they need to identify and introduce digital skills and co ...
This publication has been prepared by the Inter-Agency Group on Technical and Vocational Education and Training on skills mismatch in digitized labour markets, to support experts and policymakers who wish to engage in discussion on the potential of w ...
Today, opportunities abound for greater use of technology in assessment and credentialing to enhance the impact of TVET on economic and social development programmes. In the past, it has often been observed that the impact of TVET on social and econo ...
A practical guide
Technology has altered many aspects of life, including education and training. As a result of technological developments, technical and vocational education and training (TVET) has become more accessible to students, and the quality of education and ...
This policy brief examines the impact of the COVID-19 crisis on vocational education and training (VET)systems and how VET systems are responding in OECD countries. The brief also presents steps that governments can take in the context of this crisis ...
11 to 15 November 2019
A considerable amount of attention has been placed on Artificial Intelligence, its impact on innovations in various sectors, and its implications for the transformation of the workforce and the labour market. Many of the professions that will most li ...
Le présent document décrit la position de l’ETF sur les compétences et les aptitudes numériques ainsi que sur l’apprentissage numérique et en ligne. Dans son approche stratégique, le document considère les deux domaines d’action thémati ...
This paper describes the ETF position on digital skills and competence (DSC), and digital and online learning (DOL). In its strategic approach, the paper considers the two thematic policy areas as mutually connected and useful to modernising access t ...
This European Commission report aims to shed light on some of the key drivers which are worth taking into account when assessing the effect of new technologies on the future of work and skills. It combines a synthesis of the most recent and robust sc ...
UNESCO and the Commonwealth of Learning have been working directly with governmental agencies and institutions to support the development of national and institutional OER policies. This publication is the culmination of this. It is meant to be refer ...
Artificial Intelligence is a booming technological domain capable of altering every aspect of our social interactions. In education, AI has begun producing new teaching and learning solutions that are now undergoing testing in different contexts. Thi ...
Closing gender divides in digital skills through education
This publication seeks to expose some of these biases and put forward ideas to begin closing a digital skills gender gap that is, in most parts of the world, wide and growing. Today, women and girls are 25 per cent less likely than men to know how to ...
Learning from Cedefop’s European skills and jobs survey
This publication focuses on a topic of critical concern for policy-makers in recent years: skill mis-match. Cedefop has been active in skill mismatch research and analysis for almost a decade now, identifying significant areas of concern and contenti ...
Version 3
The ICT Competency Framework for Teachers (ICT CFT) Version 3 is a tool to guide pre- and in- service teacher training on the use of ICTs across the education system. It is intended to be adapted and contextualized to support national and institution ...
Implications for the recognition of learning across borders
Digital technologies are creating new opportunities and challenges for skills development and recognition globally. Changes in modalities of access and learning methods, massification and internationalization, are taking place at an increasingly rapi ...
Report of the UNESCO Mobile Learning Week 2018, 26-30 March 2018
All over the world, the way we educate and are educated is changing. New technologies, platforms and ways of reading the world are transforming the philosophies underpinning education pedagogies and modes of delivery. New voices, hitherto unheard, ar ...
What conclusions can we draw from international comparative indicators?
This report looks at the conditions impacting the development of digital skills based on five international comparative surveys, the results of which reveal a sample group of twelve countries whose population have particularly high levels of digital ...
Handbook: Open Educational Resources for skills development
Digital technology is gaining in importance - not only in life and work, but also in education and training. The availability of quality educational materials to prepare learners for work and life is a key factor to ensure an inclusive and equitable ...
The Education 2030 Agenda highlights the need to rethink technical and vocational education and training (TVET) and skills development. Out of the seven targets to achieve by 2030, two are directly linked to TVET. They aim to “ensure equal access t ...
The Education for All initiative concluded in 2015, but in many countries, and particularly in the developing countries, secondary education is still the preserve of the privileged few. This means that millions of adults and young people are denied t ...
Soumis par l’Autorité de l’enseignement technique et du développement des compétences, Philippines
Aux Philippines, l’Autorité de l’enseignement technique et du développement des compétences a exploité le potentiel des technologies de l’information et de la communication (TIC) pour augmenter la capacité d’absorption de l’EFTP, formu ...
Soumis par le Ministère de l’enseignement supérieur et de la formation, Afrique du Sud
En Afrique du Sud, l’élaboration des programmes d’EFTP est centralisée au niveau national. Avec les résultats et les normes déjà établis, la cartographie des programmes d’enseignement permet d’inclure les nouvelles avancées technologiq ...
Submitted by Shenzhen Polytechnic, China
Employees equipped with qualifications and competencies relating to the information and communications technology (ICT) industry are in high demand around the world. This is particularly true in Shenzhen, a global hub of ICT companies and innovation. ...
UNESCO-UNEVOC Promising Practice
The Korea Open Courseware (KOCW) is the largest platform for open educational resources (OER) in the Republic of Korea. It was set up to assist individuals wishing to access higher education learning resources by providing materials from over 224 uni ...
UNESCO-UNEVOC Promising Practice
As a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, the government of Malaysia issued a ‘Movement Control Order’ to limit interactions and prevent the spread of the deadly virus.
This included closing educational institutions to face-to-face learning. Educa ...
Soumis par Campus des Métiers, France
Le Bachelor Industrie 4.0 est un cours de formation qui répond aux défis européens dans le domaine de la maîtrise des compétences et des outils numériques. Mettant un accent particulier sur le travail collaboratif, le cours a été créé en é ...
Soumis par Fagskolen Innlandet, Norvège
Compte tenu de l’importance croissante des compétences numériques et de l’utilisation de la technologie dans le travail et la vie quotidienne, il est crucial de répondre aux exigences modernes en matière de compétences numériques et de trad ...
UNESCO-UNEVOC Promising Practice
FADIO represents a unique collaborative initiative that takes full advantage of education in a digital environment. Not all educational institutions have the resources to develop the pedagogical and technical aspects related to distance education on ...
UNESCO-UNEVOC Promising Practice
Laboratoria, a Lima-based web development company, observed a lack of female software developers in Peru and decided to set up a six-month training course for women, called Code Academy. The course is offered exclusively to young women from low-incom ...
UNESCO-UNEVOC Promising Practice
In India, women from rural communities often have little say in family and community decision-making. Skills development is a recognized medium of empowerment. However, access to TVET remains a challenge to a majority of those living in rural India. ...
As the lead United Nations Organization for education, UNESCO guides international efforts to help countries understand the role such technology can play to accelerate progress toward Sustainable Development Goal 4![]() (SDG4), a vision captured in the Qingdao Declaration
(SDG4), a vision captured in the Qingdao Declaration![]() .
.
 Artificial Intelligence for Sustainable Development
Artificial Intelligence for Sustainable Development![]()
Rapid technological advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI), as well as other advancing technologies such as robotics, cloud computing and Internet of Things, are transforming disciplines, economies and industries, and challenging ideas about what it means to be human. AI has enormous potential for social good and promoting the achievement of the SDGs if it develops in a way that benefits humanity, respects global norms and standards, and is anchored in peace and development.
Mobile Learning Week is UNESCO's flagship ICT in education conference. Held annually since 2011, the event convenes experts from around the world to share how affordable and powerful advanced technology can accelerate learning for all. A wide range of participants, including officials from Ministries of Education and ICT, international experts, representatives from major partners in the field and private companies are present to share innovative ways of learning with new technologies. The Week includes a symposium, a policy forum, workshops, strategy labs and side events.
UNESCO believes that universal access to high quality education contributes to peace, sustainable social and economic development, and intercultural dialogue. The introduction of OER provides a strategic opportunity to improve the quality of education as well as improve policy dialogue, knowledge-sharing and capacity-building. With the support of the Hewlett Foundation, UNESCO has been active in promoting OER, up to the point of the adoption of the UNESCO Recommendation on Open Educational Resources in 2019. The UNESCO Education Sector focuses on monitoring and analyzing global progress in adopting OER as well as supporting the development of national OER policies through regional and national workshops.
UNESCO's ICT-CFT Hub contains collections of OER curated by UNESCO and partner countries which are aligned to the UNESCO ICT Competency Framework for Teachers (CFT). Here you can discover content and connect with other educators who are using Information and Communication Technology (ICT) to improve teaching practice.
The UNESCO ICT Competency Framework for Teachers (ICT-CFT) is intended to inform educational policy makers, providers of professional learning and working teachers on the role of ICT in educational reform, as well as to assist Member States in developing national ICT competency standards for teachers with an ICT in Education Master Plan approach. Details on the Framework can be found at UNESCO ICT in Education![]() .
.
UNESCO regional office Bangkok ICT in education activities![]()
UNESCO Bangkok’s Asia Pacific Regional Programme on ICT in Education supports Member States in effectively using ICT to facilitate the achievement of the Education 2030 targets. The Programme focuses its efforts to implement the Asia Pacific Regional Strategy on Using ICT to Facility the Achievement of Education 2030 through four priority areas: 1) secondary education, technical vocational education and training (TVET) and higher education; 2) quality of teaching and teaching practices; 3) inclusion and equality; and 4) monitoring and evaluation.