
The UNESCO-UNEVOC International Centre: Who We Are | What We Do | Working With Us | Get in Touch
The UNEVOC Network: Learn About the Network | UNEVOC Network Directory
For Members: UNEVOC Centre Dashboard
Thematic Areas: Inclusion and Youth | Digital Transformation | Private Sector Engagement | SDGs and Greening TVET
Our Key Programmes & Projects: BILT: Bridging Innovation and Learning in TVET | Building TVET resilience | TVET Leadership Programme | WYSD: World Youth Skills Day
Past Activities: COVID-19 response | i-hubs project | TVET Global Forums | Virtual Conferences | YEM Knowledge Portal
Our Services & Resources: Publications | TVET Forum | TVET Country Profiles | TVETipedia Glossary | Innovative and Promising Practices | Toolkits for TVET Providers | Entrepreneurial Learning Guide
Events: Major TVET Events | UNEVOC Network News

Digital transformation leads to massive changes in the skill sets needed for work and life. Successful use of digital technologies is also a key factor in meeting the Sustainable Development Goals. Teaching and learning need to address the changes and challenges brought about by the introduction of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) in almost all areas. TVET institutions have to make best use of new technologies to provide adequate education. As Bill Gates said: “Teachers need to integrate technology seamlessly into the curriculum instead of viewing it as an add-on, an afterthought, or an event.” This is particularly true in TVET when it comes to preparing learners for the world of work of the present and future.
Education and training institutions at all levels need to provide every citizen with the knowledge, skills and attitudes as well as the lifelong learning opportunities required for living and working in an increasingly technology-driven environment. ICT can be a powerful tool to contribute in providing universal access to education and training. All citizens need to have 21st century skills including basic ICT skills but there is also a high need for qualified graduates with specialized IT skills in all parts of the world. For TVET systems to keep pace, and to ensure inclusive learning processes that provide access to a growing number of learners, it will be key to develop a culture of sharing and openness. In a world in which changes are taking place faster than ever before, teachers themselves are learners, no less than their students. In today's world, networking has become the most important resource – off-line and online.
Networking is the most important resource
UNESCO-UNEVOC aims to promote the use of technology by:
As new tools and technologies are introduced for imparting new skills and vocational education and training, the role of teachers and trainers is also evolving continuously. Technology might introduce newer learning paradigms but can never replace teachers and trainers. They should always be central to introduction of ICT in learning environments. In recent years, an enormous amount of learning resources has become available online for teachers, trainers and learners. At UNESCO-UNEVOC we are working to identify emerging trends, new methods and means of integrating TVET teaching whether in formal or informal settings including classrooms, workshops, or within companies. We are focusing on identifying the essential digital competencies and the skills for TVET teachers to always remain future ready.
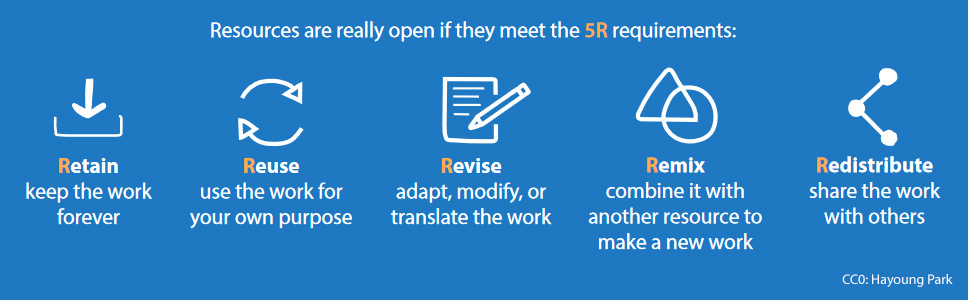
Open Educational Resources are teaching and learning materials that one can freely use and reuse, without charge.
There is an enormous wealth of learning and training materials available online. Digital technologies and the internet allow for easy sharing of such resources. The example of Wikipedia shows the power of collaborative editing to jointly create open knowledge resources. However, most educational materials are still published under restrictive traditional copyright which does not allow for legal sharing and re-editing. The idea of open licensing aims to turn the copyright restriction around: Instead of always having to ask the copyright holder for permission, an open license explicitly specifies under what circumstances and conditions a work can be used and reused - it thus encourages the sharing of resources. Ultimately, it leads to OER-enabled pedagogy![]() . In TVET the potential of OER and Open Educational Practices is not yet realized. Access to high-quality TVET can be improved considerably if high-quality content would be available under open licenses. OER can take many different forms: They range from textbooks to curricula, syllabi, course materials or lecture notes, assignments, tests, audio, video and animation.
. In TVET the potential of OER and Open Educational Practices is not yet realized. Access to high-quality TVET can be improved considerably if high-quality content would be available under open licenses. OER can take many different forms: They range from textbooks to curricula, syllabi, course materials or lecture notes, assignments, tests, audio, video and animation.

The term Open Educational Resources was first coined in 2002. Subsequent conferences recognized that OER can play a key role towards achieving the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, and above all Sustainable Development Goal 4 on Quality Education. The first World OER Congress in 2012 called on governments to ensure that public spending results in the creation of public educational materials:
Governments/competent authorities can create substantial benefits for their citizens by ensuring that educational materials developed with public funds be made available under open licenses (with any restrictions they deem necessary) in order to maximize the impact of the investment (2012 Paris OER Declaration
.![]() )
)
At UNESCO’s General Conference in November 2019 Member States adopted a Recommendation on Open Educational Resources![]() . This new standard setting instrument has five objectives: (i) Building capacity of stakeholders to create access, use, adapt and redistribute OER; (ii) Developing supportive policy; (iii) Encouraging inclusive and equitable quality OER; (iv) Nurturing the creation of sustainability models for OER; and (v) Facilitating international cooperation.
. This new standard setting instrument has five objectives: (i) Building capacity of stakeholders to create access, use, adapt and redistribute OER; (ii) Developing supportive policy; (iii) Encouraging inclusive and equitable quality OER; (iv) Nurturing the creation of sustainability models for OER; and (v) Facilitating international cooperation.
A study commissioned by UNESCO-UNEVOC in 2018 found that the OER concept is still widely unknown among TVET stakeholders - while at the same time it is regarded as highly promising in terms of improving access to high-quality TVET. Our brochure aims to help understand and utilize OER.
Handbook: Open Educational Resources for skills development
Digital technology is gaining in importance - not only in life and work, but also in education and training. The availability of quality educational materials to prepare learners for work and life is a key factor to ensure an inclusive and equitable ...
There is an enormous amount of educational and training-related content available online. We have compiled a commented list of OER platforms and services providing openly licensed content for TVET.
ICT CFT/OER Hub - Online resource
This hub contains collections of Open Educational Resources (OER) curated by UNESCO and partner countries, which are aligned with the UNESCO ICT Competency Framework for Teachers (CFT). Here you can discover content and connect with other educators w ...
Publicly available generative AI (GenAI) tools are rapidly emerging, and the release of iterative versions is outpacing the adaptation of national regulatory frameworks. The absence of national regulations on GenAI in most countries leaves the data p ...
Guidelines for countries to undertake a strategic planning framework
These guidelines follow the publication of Digital Transformation of TVET and Skills Development Systems in Africa - Guidelines for countries to undertake a situational analysis (‘the Situational Analysis Guidelines’).
In concert with the situ ...
Guidelines for countries to undertake a situational analysis
The Pan African Initiative for the Digital Transformation of TVET and Skills Development Systems in Africa (‘the initiative’) was launched on 9 March 2021. The initiative’s overall objective is to create an ecosystem that will enable and accele ...
While the key role of digital competence is well-acknowledged in meeting the needs of Industry 4.0 and the new demands of the digital economy and society, COVID-19 has exposed, with urgency and intensity, the importance of building digital competence ...
Digitalization has led to extensive changes in the skills required for work and life. For technical and vocational education and training (TVET) institutions to remain relevant and attractive, they need to identify and introduce digital skills and co ...
This publication has been prepared by the Inter-Agency Group on Technical and Vocational Education and Training on skills mismatch in digitized labour markets, to support experts and policymakers who wish to engage in discussion on the potential of w ...
Today, opportunities abound for greater use of technology in assessment and credentialing to enhance the impact of TVET on economic and social development programmes. In the past, it has often been observed that the impact of TVET on social and econo ...
A practical guide
Technology has altered many aspects of life, including education and training. As a result of technological developments, technical and vocational education and training (TVET) has become more accessible to students, and the quality of education and ...
This policy brief examines the impact of the COVID-19 crisis on vocational education and training (VET)systems and how VET systems are responding in OECD countries. The brief also presents steps that governments can take in the context of this crisis ...
11 to 15 November 2019
A considerable amount of attention has been placed on Artificial Intelligence, its impact on innovations in various sectors, and its implications for the transformation of the workforce and the labour market. Many of the professions that will most li ...
Le présent document décrit la position de l’ETF sur les compétences et les aptitudes numériques ainsi que sur l’apprentissage numérique et en ligne. Dans son approche stratégique, le document considère les deux domaines d’action thémati ...
This paper describes the ETF position on digital skills and competence (DSC), and digital and online learning (DOL). In its strategic approach, the paper considers the two thematic policy areas as mutually connected and useful to modernising access t ...
This European Commission report aims to shed light on some of the key drivers which are worth taking into account when assessing the effect of new technologies on the future of work and skills. It combines a synthesis of the most recent and robust sc ...
UNESCO and the Commonwealth of Learning have been working directly with governmental agencies and institutions to support the development of national and institutional OER policies. This publication is the culmination of this. It is meant to be refer ...
Artificial Intelligence is a booming technological domain capable of altering every aspect of our social interactions. In education, AI has begun producing new teaching and learning solutions that are now undergoing testing in different contexts. Thi ...
Closing gender divides in digital skills through education
This publication seeks to expose some of these biases and put forward ideas to begin closing a digital skills gender gap that is, in most parts of the world, wide and growing. Today, women and girls are 25 per cent less likely than men to know how to ...
Learning from Cedefop’s European skills and jobs survey
This publication focuses on a topic of critical concern for policy-makers in recent years: skill mis-match. Cedefop has been active in skill mismatch research and analysis for almost a decade now, identifying significant areas of concern and contenti ...
Version 3
The ICT Competency Framework for Teachers (ICT CFT) Version 3 is a tool to guide pre- and in- service teacher training on the use of ICTs across the education system. It is intended to be adapted and contextualized to support national and institution ...
Implications for the recognition of learning across borders
Digital technologies are creating new opportunities and challenges for skills development and recognition globally. Changes in modalities of access and learning methods, massification and internationalization, are taking place at an increasingly rapi ...
Report of the UNESCO Mobile Learning Week 2018, 26-30 March 2018
All over the world, the way we educate and are educated is changing. New technologies, platforms and ways of reading the world are transforming the philosophies underpinning education pedagogies and modes of delivery. New voices, hitherto unheard, ar ...
What conclusions can we draw from international comparative indicators?
This report looks at the conditions impacting the development of digital skills based on five international comparative surveys, the results of which reveal a sample group of twelve countries whose population have particularly high levels of digital ...
Handbook: Open Educational Resources for skills development
Digital technology is gaining in importance - not only in life and work, but also in education and training. The availability of quality educational materials to prepare learners for work and life is a key factor to ensure an inclusive and equitable ...
The Education 2030 Agenda highlights the need to rethink technical and vocational education and training (TVET) and skills development. Out of the seven targets to achieve by 2030, two are directly linked to TVET. They aim to “ensure equal access t ...
The Education for All initiative concluded in 2015, but in many countries, and particularly in the developing countries, secondary education is still the preserve of the privileged few. This means that millions of adults and young people are denied t ...
Submitted by the Technical Education and Skills Development Authority, Philippines
In the Philippines, the Technical Education and Skills Development Authority (TESDA) has leveraged the potential of information and communication technology (ICT) to increase the absorptive capacity for TVET delivery, shape future curricula in terms ...
Submitted by Department of Higher Education and Training, South Africa
In South Africa, TVET curricula are developed centrally at the national level. With the outcomes and standards already established, curriculum mapping adds new technological developments to existing curricula without the need for large-scale changes. ...
Submitted by Shenzhen Polytechnic, China
Employees equipped with qualifications and competencies relating to the information and communications technology (ICT) industry are in high demand around the world. This is particularly true in Shenzhen, a global hub of ICT companies and innovation. ...
UNESCO-UNEVOC Promising Practice
The Korea Open Courseware (KOCW) is the largest platform for open educational resources (OER) in the Republic of Korea. It was set up to assist individuals wishing to access higher education learning resources by providing materials from over 224 uni ...
UNESCO-UNEVOC Promising Practice
As a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, the government of Malaysia issued a ‘Movement Control Order’ to limit interactions and prevent the spread of the deadly virus.
This included closing educational institutions to face-to-face learning. Educa ...
Submitted by Campus des Métiers, France
Bachelor Industry 4.0 is a training course that responds to European challenges in the field of mastering digital skills and tools. With a special focus on collaborative work, the course has been created in close collaboration with professional secto ...
Submitted by Fagskolen Innlandet, Norway
In view of the increasing prominence of digital skills and use of technology in work and daily life, it is crucial to meet modern digital skills requirements and to reflect the latest technological evolutions in TVET training. As a response, Fagskole ...
UNESCO-UNEVOC Promising Practice
FADIO represents a unique collaborative initiative that takes full advantage of education in a digital environment. Not all educational institutions have the resources to develop the pedagogical and technical aspects related to distance education on ...
UNESCO-UNEVOC Promising Practice
Laboratoria, a Lima-based web development company, observed a lack of female software developers in Peru and decided to set up a six-month training course for women, called Code Academy. The course is offered exclusively to young women from low-incom ...
UNESCO-UNEVOC Promising Practice
In India, women from rural communities often have little say in family and community decision-making. Skills development is a recognized medium of empowerment. However, access to TVET remains a challenge to a majority of those living in rural India. ...
As the lead United Nations Organization for education, UNESCO guides international efforts to help countries understand the role such technology can play to accelerate progress toward Sustainable Development Goal 4![]() (SDG4), a vision captured in the Qingdao Declaration
(SDG4), a vision captured in the Qingdao Declaration![]() .
.
 Artificial Intelligence for Sustainable Development
Artificial Intelligence for Sustainable Development![]()
Rapid technological advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI), as well as other advancing technologies such as robotics, cloud computing and Internet of Things, are transforming disciplines, economies and industries, and challenging ideas about what it means to be human. AI has enormous potential for social good and promoting the achievement of the SDGs if it develops in a way that benefits humanity, respects global norms and standards, and is anchored in peace and development.
Mobile Learning Week is UNESCO's flagship ICT in education conference. Held annually since 2011, the event convenes experts from around the world to share how affordable and powerful advanced technology can accelerate learning for all. A wide range of participants, including officials from Ministries of Education and ICT, international experts, representatives from major partners in the field and private companies are present to share innovative ways of learning with new technologies. The Week includes a symposium, a policy forum, workshops, strategy labs and side events.
UNESCO believes that universal access to high quality education contributes to peace, sustainable social and economic development, and intercultural dialogue. The introduction of OER provides a strategic opportunity to improve the quality of education as well as improve policy dialogue, knowledge-sharing and capacity-building. With the support of the Hewlett Foundation, UNESCO has been active in promoting OER, up to the point of the adoption of the UNESCO Recommendation on Open Educational Resources in 2019. The UNESCO Education Sector focuses on monitoring and analyzing global progress in adopting OER as well as supporting the development of national OER policies through regional and national workshops.
UNESCO's ICT-CFT Hub contains collections of OER curated by UNESCO and partner countries which are aligned to the UNESCO ICT Competency Framework for Teachers (CFT). Here you can discover content and connect with other educators who are using Information and Communication Technology (ICT) to improve teaching practice.
The UNESCO ICT Competency Framework for Teachers (ICT-CFT) is intended to inform educational policy makers, providers of professional learning and working teachers on the role of ICT in educational reform, as well as to assist Member States in developing national ICT competency standards for teachers with an ICT in Education Master Plan approach. Details on the Framework can be found at UNESCO ICT in Education![]() .
.
UNESCO regional office Bangkok ICT in education activities![]()
UNESCO Bangkok’s Asia Pacific Regional Programme on ICT in Education supports Member States in effectively using ICT to facilitate the achievement of the Education 2030 targets. The Programme focuses its efforts to implement the Asia Pacific Regional Strategy on Using ICT to Facility the Achievement of Education 2030 through four priority areas: 1) secondary education, technical vocational education and training (TVET) and higher education; 2) quality of teaching and teaching practices; 3) inclusion and equality; and 4) monitoring and evaluation.